
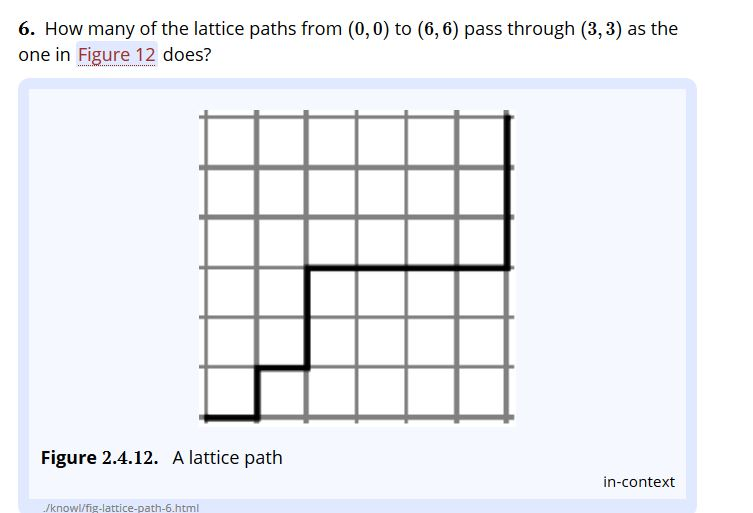
Complete lattices appear in many applications in mathematics and computer science.
Specifically, every non-empty finite lattice is complete. A lattice which satisfies at least one of these properties is known as a conditionally complete lattice. In mathematics, a complete lattice is a partially ordered set in which all subsets have both a supremum (join) and an infimum (meet). In that case it serves more or less as a data structure in which you can put certain objects and prove that the desired object is also in that structure or not.Partially ordered set in which all subsets have both a supremum and infimum On the other hand lattice theory in the first sense can be used as a tool for proofs. In case of complex analysis you are probably interested in the second one if you are in the approximation of certain point sets by similar sets with sufficiently regular borders. This should be true also for the financial lattice model, which considers the grid points instead of integrating over an interval. This kind of lattice is also behind the lattice multiplication where the notion “lattice” is not taken from mathematical but from natural language.
LATTICE MATH SET THEORY FREE
every torsion free abelian group is a $\mathbb Z$ module. This would also fit into your group category. This kind of lattice is typically linked to the embedding of a module in a vector space.

Skew lattice, a noncommutative generalization of a lattice Lattice model (finance), a method for evaluating stock options that divides time into discrete intervals Lattice multiplication, a multiplication algorithm suitable for hand calculation Lattice graph, a graph that can be drawn within a repeating arrangement of pointsīethe lattice, a regular infinite tree structure Lattice (module), a module over a ring embedded in a vector space over a field Lattice (discrete subgroup), a discrete subgroup of a topological group with finite covolume Lattice (group), a repeating arrangement of points Lattice (order), a partially ordered set with unique least upper bounds and greatest lower bounds Then general definition of lattice from group theory and from different branches of mathematics Just as a periodic function of a real variable is defined by its values on an interval, an elliptic function is determined by its values on a fundamental parallelogram, which then repeat in a lattice In complex analysis, an elliptic function is a meromorphic function that is periodic in two directions.
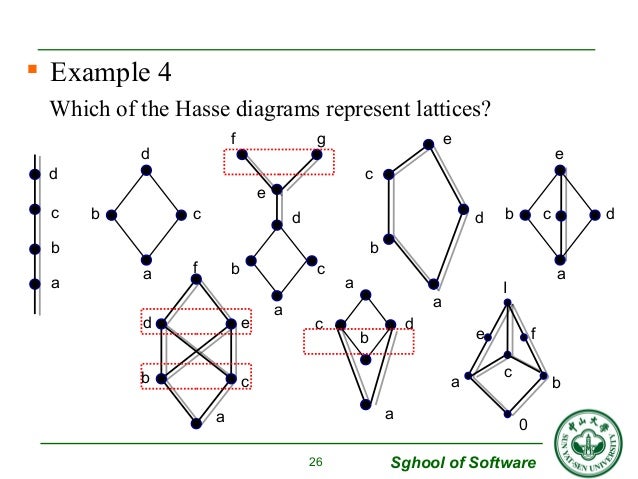
I would like to understand meaning of lattice in mathematics, for example let us consider its application, first one is Elliptic function:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
