
Index=cybersecurity hacker SPL search termsįind the word “Cybersecurity” irrespective of capitalizationįind those three words in any order irrespective of capitalizationįind the exact phrase with the given special characters, irrespective of capitalization This is the shorthand query to find the word hacker in an index called cybersecurity: For comparing two different fields.īegin by specifying the data using the parameter index, the equal sign =, and the data index of your choice: index=index_of_choice.Ĭomplex queries involve the pipe character |, which feeds the output of the previous query into the next. Similar to stats but used on metrics instead of eventsĭisplays the most/least common values of a fieldįilters search results using eval expressions. Provides statistics, grouped optionally by fields Sorts the search results by the specified fields X Use wildcards (*) to specify multiple fields.Įxtract fields according to specified regular expression(s)įilters results to those that match the search expression Returns the first/last N results, where N is a positive integerĪdds field values from an external source Returns results in a tabular output for (time-series) chartingĬalculates an expression (see Calculations) Note the decreasing number of results below: Finding entries without IPv4 address on sample data Common Search Commands Command It is a process of narrowing the data down to your focus.
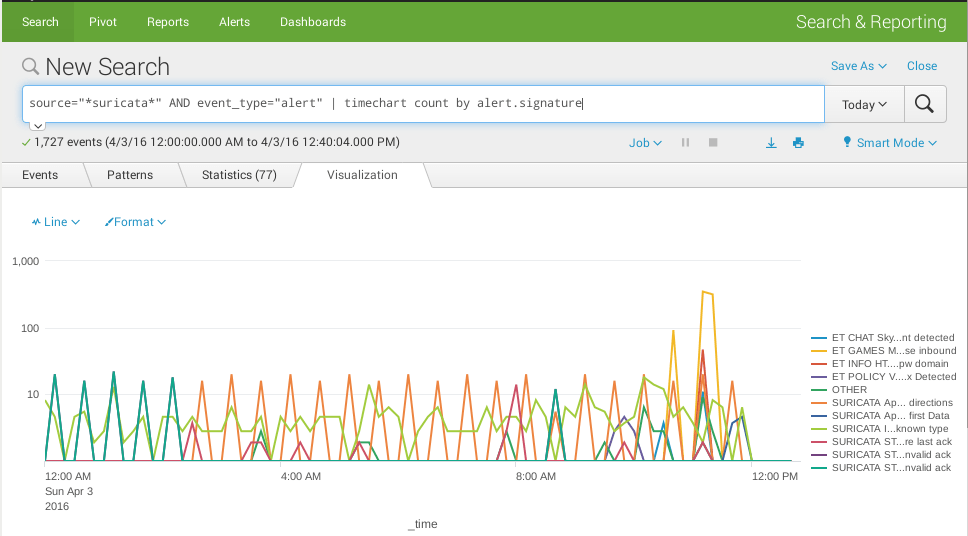
Search commands help filter unwanted events, extract additional information, calculate values, transform data, and statistically analyze the indexed data. Here is an example of an event in a web activity log: It can be a text document, configuration file, or entire stack trace. Unless you’re joining two explicit Boolean expressions, omit the AND operator because Splunk assumes the space between any two search terms to be AND.īasic Search offers a shorthand for simple keyword searches in a body of indexed data myIndex without further processing:Īn event is an entry of data representing a set of values associated with a timestamp. Splunk uses what’s called Search Processing Language (SPL), which consists of keywords, quoted phrases, Boolean expressions, wildcards (*), parameter/value pairs, and comparison expressions.
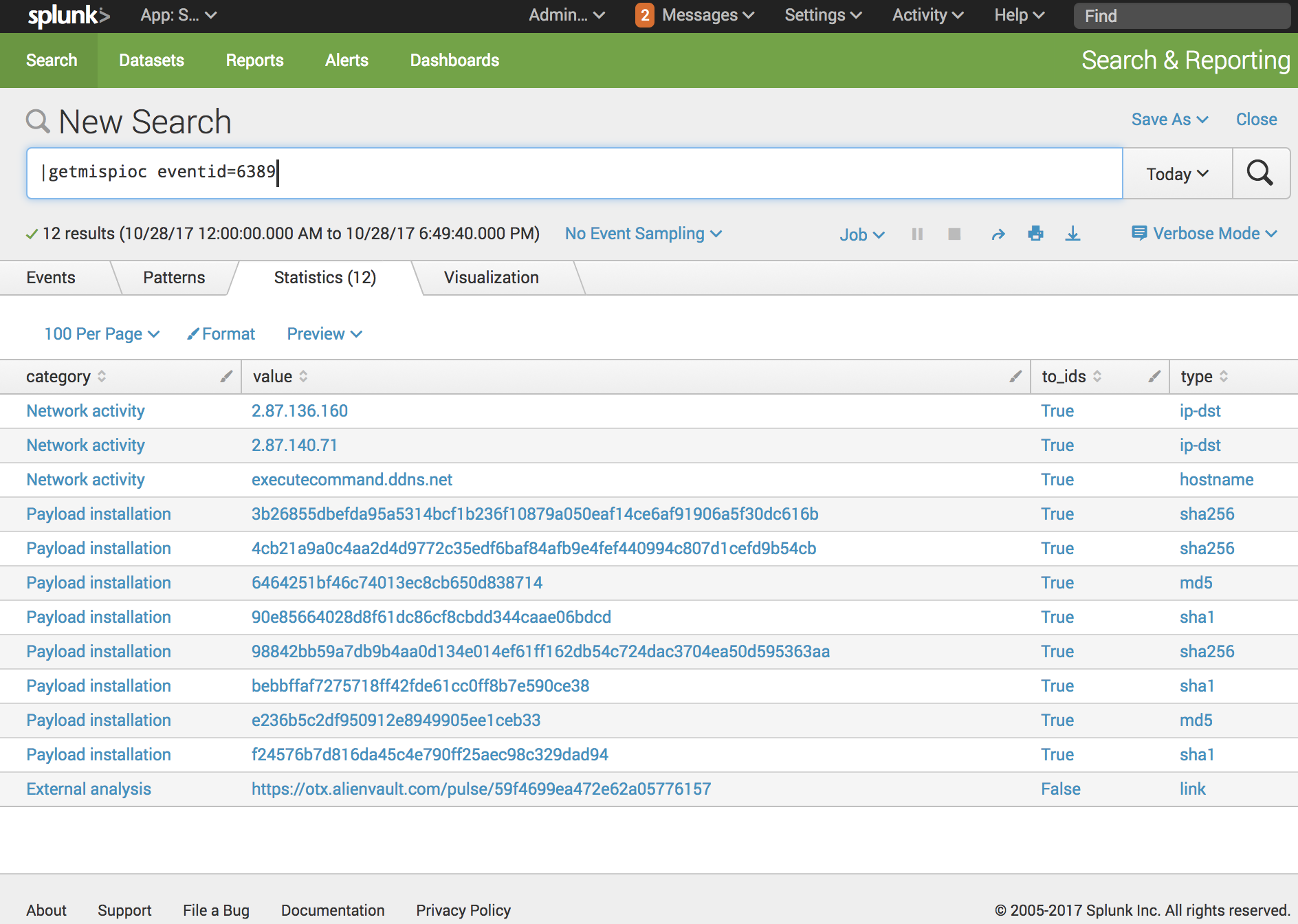
This is interpreted by SPL as a search for the text "expression" OR "with pipe".
For example, A or B is expressed as A | B.īecause pipe characters are used to separate commands in SPL, you must enclose a regular expression that uses the pipe character in quotation marks. Here are a few things that you should know about using regular expressions in Splunk searches.Ī pipe character ( | ) is used in regular expressions to specify an OR condition. You can also use regular expressions with evaluation functions such as match and replace. You can use regular expressions with the rex and regex commands.
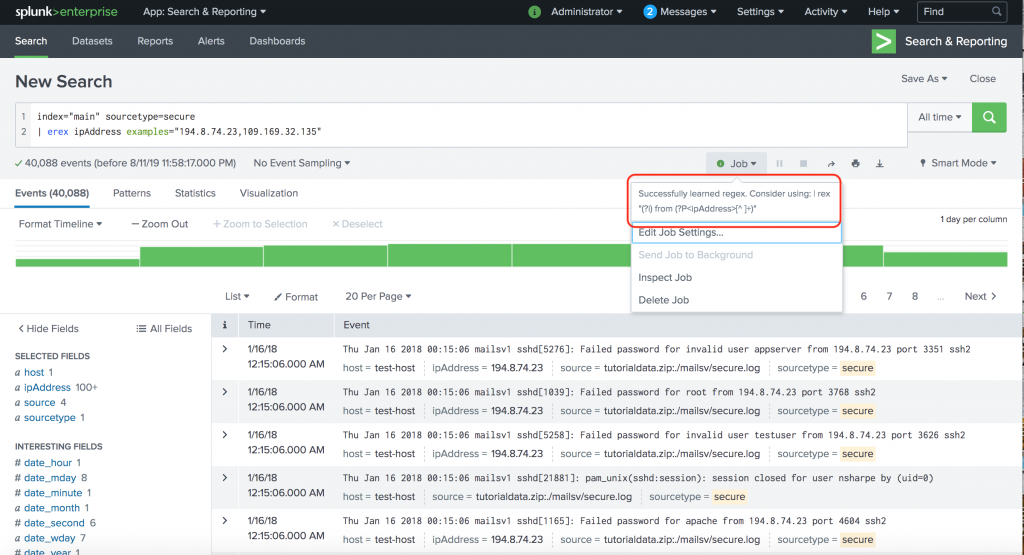
Splunk Search Processing Language (SPL) regular expressions are PCRE (Perl Compatible Regular Expressions).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
